Introduction
In the present era, the Internet of Things (IoT) is not a novel technology; rather, it has become a well-established and integral aspect of contemporary technological landscapes.
IoT originated in the late 20th century, evolving with the integration of RFID and sensor technologies. The 2000s witnessed its formal conceptualization, and since then, IoT has rapidly advanced, connecting devices globally and transforming industries with data-driven innovations.
IoT refers to the interconnected network of physical devices, vehicles, appliances, and other objects embedded with sensors, actuators, software, and network connectivity, enabling them to collect and exchange data. In simpler terms, IoT allows everyday objects to communicate and share information over the internet.
Industries such as Automotive, Finance, Smart cities, healthcare, and industrial IoT (IIoT) have witnessed profound changes through the integration of IoT technologies. Below is the number investigated by Statista Market Insights in IOT market revenue in 2018 and predicted to 2028.
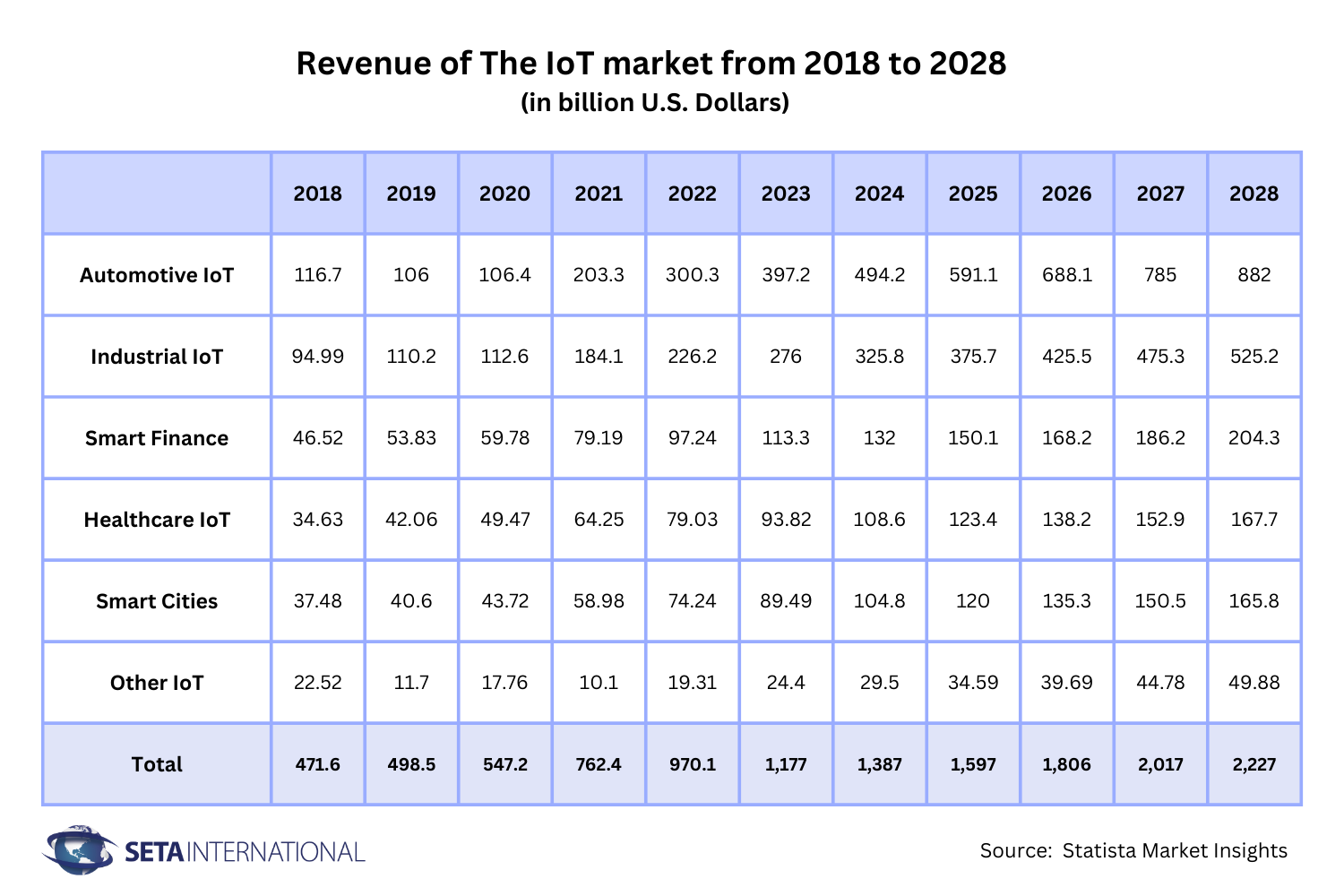

In this blog, we’ll be discussing the benefits and use cases of IoT in the top 5 industries including Automotive, Industrial, Finance, Healthcare and Smart Cities.

Automotive IoT
IoT in the automotive sector offers transformative benefits, enhancing vehicle safety, efficiency, and maintenance. Real-time monitoring and predictive analytics reduce downtime, optimize routes and fuel consumption, and enable proactive maintenance. Connected vehicles, smart parking, and advanced driver assistance systems contribute to a safer, more efficient, and technologically advanced driving experience.

Connected Fleet Management
Implementation: Equipping vehicles with IoT devices and sensors.
Functionality: Real-time tracking of vehicles, monitoring fuel consumption, and optimizing routes for improved efficiency. This technology enables proactive maintenance scheduling and enhances overall fleet management.
Predictive Maintenance
Implementation: Integrating IoT sensors into critical vehicle components.
Functionality: Continuous monitoring of engine health, tire pressure, and other vital parameters. Predictive analytics anticipate potential issues, enabling timely maintenance and reducing the risk of unexpected breakdowns.
Smart Parking Solutions
Implementation: Deploying IoT sensors in parking spaces and within vehicles.
Functionality: Real-time data on parking space availability is shared with drivers, reducing search time. Vehicles equipped with IoT can autonomously find and park in available spaces, optimizing parking in urban environments.
Enhanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS)
Implementation: Integration of IoT sensors, cameras, and radar systems in vehicles.
Functionality: ADAS uses real-time data to provide features like adaptive cruise control, lane departure warnings, and collision avoidance. Enhances driver safety by providing timely alerts and interventions.
Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) Communication
Implementation: Enabling vehicles to communicate with each other and with infrastructures.
Functionality: Facilitates V2V communication for collision avoidance and traffic optimization. V2I communication allows vehicles to interact with traffic signals, enhancing traffic flow and safety.
These use cases showcase how IoT technologies are transforming the automotive sector by improving vehicle management, safety, and efficiency. The integration of IoT devices and data-driven solutions is driving innovation and reshaping the way vehicles operate and interact with their surroundings.
Industrial IoT (IIoT)
IIoT revolutionizes industries by enhancing operational efficiency, predictive maintenance, and overall productivity. Real-time monitoring and data analytics optimize production processes, minimize downtime, and improve resource utilization. Connected devices enable smarter decision-making, fostering a more agile and competitive industrial landscape with increased automation, safety, and sustainability.

Predictive Maintenance
Implementation: Embedding sensors in machinery and equipment.
Functionality: Continuous monitoring of equipment conditions. Predictive analytics anticipate potential failures, allowing for timely maintenance and minimizing downtime.
Asset Tracking and Management
Implementation: Integrating IoT-enabled tags and sensors on industrial assets.
Functionality: Real-time tracking of assets within the facility, optimizing inventory management, and reducing the risk of loss or theft.
Smart Manufacturing (Industry 4.0)
Implementation: Connecting machines and systems through IoT.
Functionality: Enables data-driven decision-making, automation, and synchronization of manufacturing processes for improved efficiency, quality, and responsiveness.
Energy Management and Sustainability
Implementation: Installing sensors to monitor energy consumption.
Functionality: Optimizes energy usage, identifies areas for improvement, and supports sustainable practices by reducing waste and improving overall resource efficiency.
Supply Chain Visibility
Implementation: Deploying IoT devices across the supply chain.
Functionality: Real-time tracking of goods, monitoring conditions such as temperature and humidity. Enhances visibility, reduces lead times, and improves overall supply chain efficiency.
These use cases illustrate how Industrial IoT (IIoT) is transforming the industrial sector by improving asset management, operational efficiency, and sustainability, ultimately fostering a more agile and competitive manufacturing environment.
Smart finance
In the smart finance sector, IoT brings about revolutionary benefits. Real-time data analytics and IoT-enabled devices enhance personalized services, streamline transactions, and fortify security. This synergy promotes cost-efficient operations, proactive fraud detection, and an overall heightened user experience, shaping a future of intelligent, secure, and client-centric financial services.

Personalized Banking Services
Implementation: Integrating IoT devices for personalized financial insights.
Functionality: Analyzing user behavior and preferences to offer tailored financial advice, services, and product recommendations.
Smart ATMs
Implementation: Equipping ATMs with IoT sensors and connectivity.
Functionality: Remote monitoring of ATM status, predictive maintenance, and real-time alerts for potential issues.
Fraud Detection and Prevention
Implementation: Utilizing IoT for continuous monitoring of transaction data.
Functionality: Detecting unusual patterns or anomalies in real-time, enabling swift response and minimizing the risk of fraudulent activities.
Contactless Payments
Implementation: Integrating IoT in payment systems and devices.
Functionality: Facilitating secure contactless payments through wearable devices, smartphones, or IoT-enabled cards, enhancing convenience and reducing physical contact.
Automated Financial Transactions
Implementation: Deploying IoT for automated financial processes.
Functionality: Streamlining routine transactions, such as bill payments and fund transfers, through IoT-connected devices, improving efficiency and reducing manual intervention.
These use cases exemplify how IoT is reshaping the smart finance sector, providing innovative solutions for personalization, security, and efficiency, ultimately enhancing the overall user experience in the world of financial services.
Healthcare
In healthcare, IoT delivers transformative benefits by enhancing patient care, improving operational efficiency, and fostering innovation. Real-time patient monitoring, remote diagnostics, and data-driven insights empower healthcare professionals. IoT’s integration streamlines processes, reduces costs, and contributes to a patient-centric approach, ultimately advancing the quality and accessibility of healthcare services.

Remote Patient Monitoring
Implementation: Wearable IoT devices and sensors.
Functionality: Continuous monitoring of vital signs, enabling healthcare providers to remotely track and manage patients with chronic conditions, improving care and reducing hospitalizations.
Smart Medical Devices
Implementation: Integration of IoT in medical equipment.
Functionality: Connected devices such as smart infusion pumps and continuous glucose monitors enhance accuracy, automate data collection, and enable real-time adjustments.
Asset Tracking and Management
Implementation: RFID and IoT-enabled tags on medical equipment.
Functionality: Real-time tracking of medical assets, optimizing inventory management, reducing loss, and ensuring the availability of critical equipment.
Predictive Maintenance for Healthcare Facilities
Implementation: IoT sensors in hospital infrastructure.
Functionality: Continuous monitoring of facility equipment to predict and prevent potential failures, ensuring the uninterrupted operation of critical systems.
Telemedicine and Virtual Health
Implementation: IoT-enabled devices for remote consultations.
Functionality: Facilitates virtual doctor-patient interactions, remote diagnostics, and monitoring, enhancing access to healthcare services and providing timely interventions.
These use cases underscore how IoT is revolutionizing healthcare, offering solutions that improve patient outcomes, enhance operational efficiency, and contribute to the advancement of telemedicine and remote patient care.
Smart Cities
In smart cities, IoT delivers optimizing urban living through enhanced efficiency, sustainability, and connectivity. Real-time data from IoT sensors enables intelligent infrastructure management, improving traffic flow, waste management, and public services. This interconnected ecosystem fosters innovation, resource optimization, and a higher quality of life for residents.

Smart Traffic Management
Implementation: IoT-connected sensors and cameras.
Functionality: Real-time traffic monitoring, optimization of signal timings, and adaptive traffic management to reduce congestion and enhance overall traffic flow.
Waste Management Optimization
Implementation: IoT sensors in waste bins.
Functionality: Monitoring waste levels, optimizing collection routes, and reducing operational costs for more efficient waste management.
Public Safety and Surveillance
Implementation: IoT-enabled surveillance cameras and sensors.
Functionality: Enhancing public safety through real-time monitoring, video analytics, and immediate response to security incidents.
Smart Street Lighting
Implementation: IoT-connected streetlights.
Functionality: Adaptive lighting based on traffic conditions, reducing energy consumption and contributing to sustainability goals.
Environmental Monitoring
Implementation: Deploying IoT sensors for air and water quality monitoring.
Functionality: Real-time data collection on environmental parameters to inform decision-making for pollution control and urban planning.
These use cases illustrate how IoT is reshaping urban landscapes, optimizing resource management, enhancing safety, and fostering sustainability in smart cities.
Conclusion
In summary, IoT innovation has a disruptive effect on a wide range of industries, including smart cities, smart finance, smart automotive, and smart industrial. The enhanced safety, connection, and efficiency are just a few examples of the IoT’s many benefits.
SETA’s proficiency in IoT development for industrial and automotive applications places them in a position to play a significant role in influencing the direction of industries as we watch this change take place. To help bring in a future where IoT continues to redefine and enrich many different sectors, get in touch with SETA for swift advice and insights from their specialists.