Risk management is the process of identifying, assessing and controlling threats to an organization’s capital and earnings. These risks stem from a variety of sources including financial uncertainties, legal liabilities, technology issues, strategic management errors, accidents and natural disasters.
A successful risk management program helps an organization consider the full range of risks it faces. Risk management also examines the relationship between risks and the cascading impact they could have on an organization’s strategic goals.
In our latest Open Talk session, Mr. Harry Vu – PMO Head and Ms. Huyen Doan have drawn a clear image of Risk Management in a project.
What’s a risk?
Any time there’s anything that might occur on your project and change the outcome of a project activity, we call that a risk. However, not all risks are negative. Some events where you need to find an easier way to finish a task or in some situations you need to lower the prices for certain positions in a project. When this happens, we call it an opportunity … but it’s still handled just like a risk.
So what defines a risk?
“If some event or condition occurs, then a specific negative impact or consequence to program objectives will result”
Let’s take an example: While developing the system. If the program cannot achieve the anticipated wing skin structural properties (condition), then wing weight will increase or the aircraft maneuvering envelope will be reduced (consequence).
How to deal with risk?
Avoid
If you can prevent it from happening, it definitely won’t hurt your project. For instance, if there is a front-end developer who has a bad coding skill, you could choose to get him out of the project. However, it’s not always possible to avoid a risk in real life.
Mitigate
This way, you could take some actions that will cause it to do as little damage as possible
Transfer
Let someone else to deal with the risk for you (or let’s say “pay”)
Accept
Just nod your head “you can’t do anything with this situation” and accept the consequences
How to plan for risk management?
A successful risk management plan tells you how you’re going to handle risk on your project—which you probably guessed. It also says how you’ll assess risk on the project, who’s responsible for doing it, and how often you’ll do risk planning.
Since you will have to discuss with your team about risk managing throughout the project. You should always pay attention to all the possible unexpected situations. If a Project Manager cannot rank the risks in terms of importance as there are many risks in one project, the project will definitely fail. What you should do is to write down all your worries, and spend time discussing with your project team what should be concerned the most.
Identifying risks
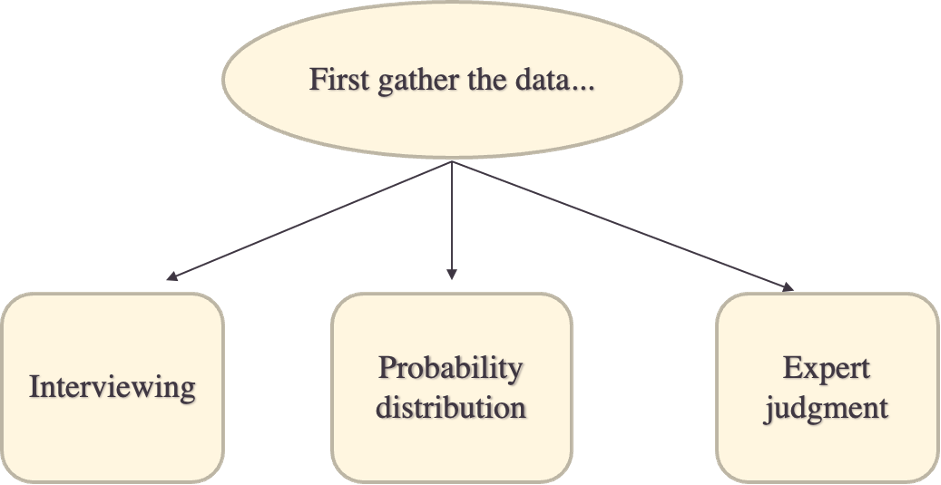
When identifying risks for your project. You should always ask: What could happen to your project? And in order to address this question, do the information gathering:
+ Brainstorming: get every team member names the possible risks, from different perspectives
+ Interviews: prepare a list of questions to ask each team member, including code quality, timeline, deployment, …
+ The Delphi technique: ask an expert about the possible risks
+ Root cause identification: analyze each risk and figure out the what’s behind it
There are some diagrams and charts that can help in identifying risks:

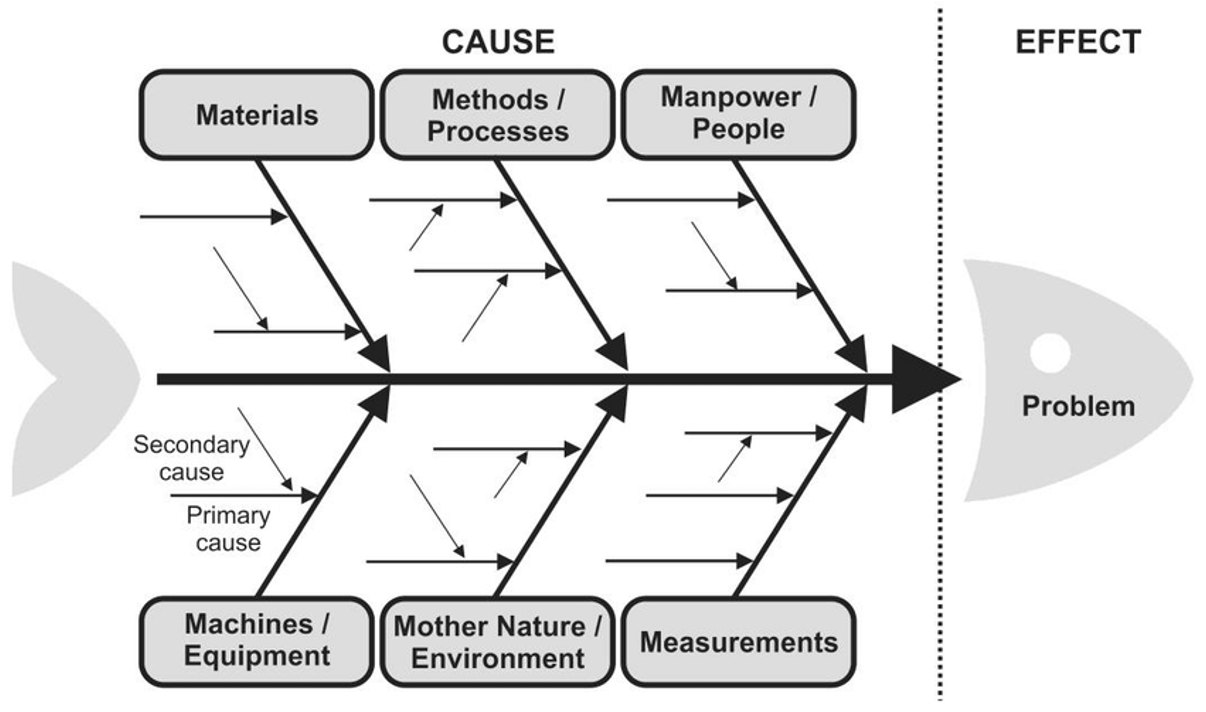
Next step, you should put it in the risk register table. It’s a good idea for your Identify Risks meetings to include a discussion of how to respond to the risks
| Identified Risks | Root causes | Potential Responses |
| 1. Clients stop contract (complain ab the code quality) | Member’s skill, carelessness | Peer review, apply QA process |
| 2…. |
Perform Qualitative Risk Analysis
Perform Qualitative Risk Analysis helps you prioritize each risk and figure out its probability and impact
- Risk data quality assessment: make sure that the information you’re using in your risk assessment is accurate
- Risk urgency assessment: check out how soon you’re going to need to take care of a particular risk.
- Expert judgment: sometimes it makes sense to bring in outside experts to check out the validity of your risk assessment data.
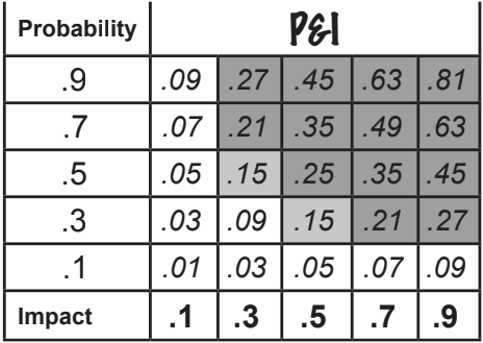
- Risk probability and impact assessment: assess the probability assessment involves estimating the likelihood of a risk occurring, also the impact assessment estimates the effects of a risk event on a project objective
- Probability and impact matrix: is a table where all of your risks are plotted out according to the values you assign
Risk = Impact x Probability
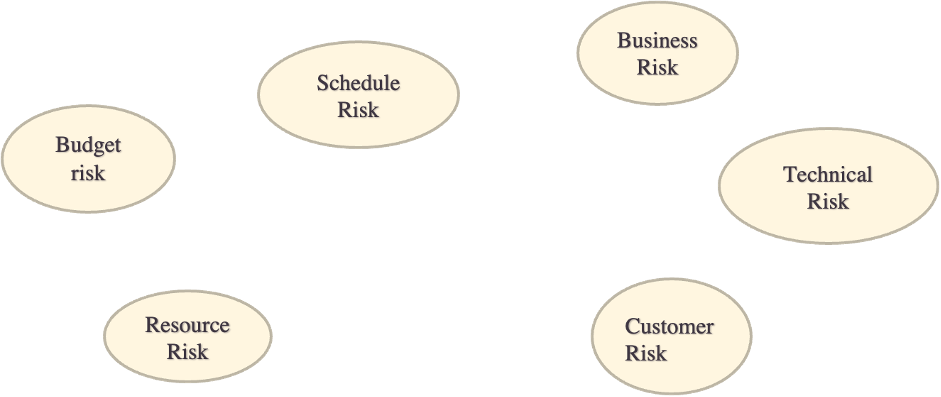
- Risk categorization: group your risks so that you can come up with a better strategy for dealing with them by the phase of the project and by the source of the risk.
Perform Quantitative Risk Analysis
A quantitative assessment is a risk analysis performed with a focus on numerical values of the risks present. It relies on data, which is used to analyze risk to budget, deadline, and resource..
- Sensitivity analysis: is the process of estimating how target variables change in relation to changes in input variables. It allows us to determine which risks have a bigger impact on the project. People generally use tornado diagrams to look at a project’s sensitivity.
- Expected monetary value analysis (EMV): it examines costs of all of the paths might take through the project (depending on which risks occur) and assign a monetary value to each decision.
EMV = P x I
| Risks | Probability | Impact |
| 1. Device is broken | 10% | Cost 800$ to buy/fix |
| 2. |
An example of EMV table: EMV= 10% x –800 = -80$
Risk Response
Exploit
Act in ways that will help increase the chances of it occurring.
Share
Working with others outside of your project who could also benefit from it to try to exploit it.
Enhance
Try to make the opportunity more probable by influencing its triggers.
Accept
And don’t forget to update the risk register
Control Risks
Risk Reassessment
Regularly scheduled reassessment meetings to go over all of the information and see if the risk register still holds true:
- Identifying new risks
- Evaluating current risks
- Evaluating the risk management process
- Closing risks
Reserve analysis
- Know how much money you have set aside for risk responses
- As you spend it, be sure to subtract it so you know if you have enough to cover all of your remaining risks.
Risk Audits
Take a look at your risk response strategies to judge how effective they are.
- Was the risk management planning sufficient?
- Did the team do a good job in identifying risks?
- Were the probability and impact (PxI) tables appropriate for the project?
- Was the selected strategy effective?
- Did the risk event occur as expected?
Technical performance measurement
Compare the performance of your project with its planned performance. Then, determine whether your progress is on track. If not, that might be a risk!
Meetings
The meetings should happen throughout the entire project and every single status meeting should have risk review on the agenda.
Copyrights by SETA International, please credit when taking out.
👉 SETA International is exploring new market sectors regional and international. We provide end-to-end technology solutions and services for AI, VR/AR, IOT, web, mobile and cloud.
—
✉️contact@setacinq.vn
🔗seta-international.com









