Scrum definition
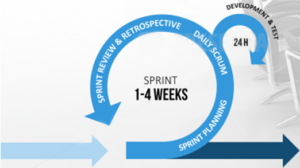
Scrum framework consist of:
- Scrum Teams and their associated roles, events, artifacts, and rules.
- The rules of Scrum bind together the events, roles, and artifacts, governing the relationships and interaction between them.
Scrum Theory
Transparency
- Main aspects of the process must be defined by a common standard.
- A common language that refers to the process has to be shared by all participants.
- A common definition of “Done” for those performing work and accepting the work product.
Inspection
- Scrum users must frequently inspect Scrum artifacts and process towards as Sprint Goal.
- Inspections should not be so frequent that they get in the way of the work.
- Inspections are more effective when diligently performed by skilled inspectors at the point of work.
Adaption
- Process or the material being processed must be adjusted if an inspection determines that on or more aspects of a process deviate outside acceptable limits and the resulting product will be unacceptable.
- Sprint Planning
- Daily Scrum
- Sprint Review
- Sprint Retrospective
Scrum value
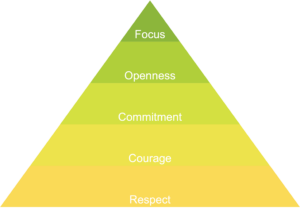
- Everyone focuses on the work of the Sprint and the goals of the Scrum Team.
- The Scrum Team and its stakeholders agree to be open about all the work and the challenges with performing the work.
- People personally commit to achieving the goals of the Scrum Team.
- The Scrum Team members have courage to do the right thing and work on tough problems.
- Scrum Team members respect each other to be capable, independent people.
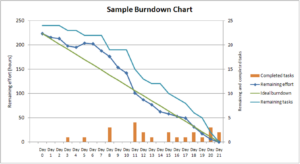
Burn-down chart
Scrum events
- The Sprint
- Sprint Planning
- Daily Scrum
- Sprint Review
- Sprint Retrospective
Note:
- All events are time-boxed events with a maximum duration.
- Once a Sprint begins, its duration is fixed and cannot be shortened or lengthened.
- An appropriate amount of time is spent without allowing waste in the process.
Scrum events – Process
- The Sprint
- Sprint Planning
- Daily Scrum
- Sprint Review
- Sprint Retrospective
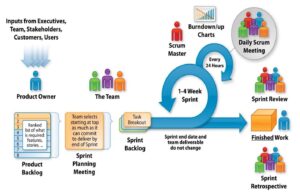
Scrum – sprint

Centerpiece of the Scrum process:
- Time-box of max. 4 weeks or less.
- During this period, a “Done” useable and potentially releasable product increment is created.
- All Sprints have the same duration, a new Sprint starts. immediately after the conclusion of the previous one.
Sprint Cancellation

A Sprint can be cancelled before the Sprint time-box is over
- Only the Product Owner has the authority to cancel the Sprint.
- The company changes direction or if market or technology conditions change.
- Sprint goal has become obsolete.
- All “Done” Product Backlog items are reviewed. If part of the work is potentially releasable, the Product Owner accepts its. All incomplete Product Backlog items are re-estimated and put back on the Product Backlog.
Scrum Process – Sprint Planning
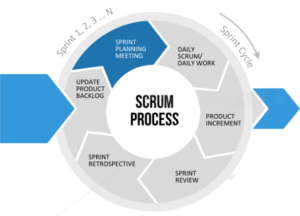
- For entire Scrum Team
- Time-box: 8 hrs (usually less for shorter Sprint)
- Consists of two topics:
-What will be delivered
-How it will be delivered
- Plan only for Sprint and not for entire product
Scrum Process – Daily Scrum
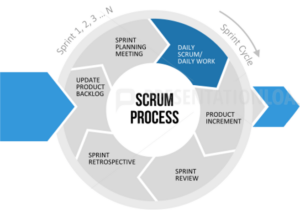
- For Dev Team. Usually held at the same place & time
- Time-box: 15 mins
- Team update each other on three questions:
-What I’ve done that helps meet Sprint Goal
-What I will do that helps meeting Sprint Goal
-Any impediments that prevent meeting Sprint Goal
Scrum Process – Product Increment
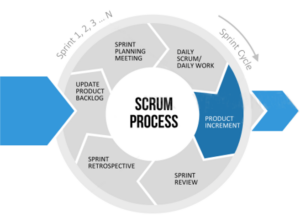
- The Increment is the sum of all the Product Backlog items competed during a Sprint, included the value of the Increment of all previous Sprints.
- At the end of a Sprint, the new Increment must be “Done”
Scrum Process – Sprint Review
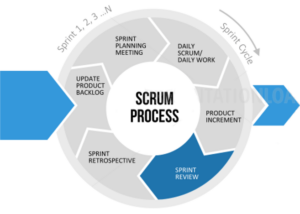
- For Scrum Team and Stakeholders
- Time-box: 4 hrs (usually less for shorter Sprints)
- Collaborate about what was done in Sprint
- Collaborate on the next things that could be done
- Get feedback that may affect Product Backlog
- Product Owner tracks total work remaining
Scrum Process – Sprint Retrospective
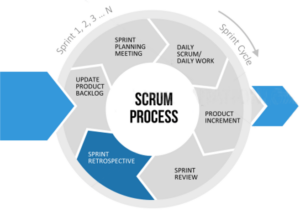
- For Scrum Team
- Time-box: 3 hrs (usually less for shorter Sprints)
- Inspect for improvements to be made for next Sprint
- Adapt definition of “Done” as required
- Three questions being asked in the retrospective:
-What went good?
-What can be improved?
-What is improvement action?
Scrum Process – Update Product Backlog
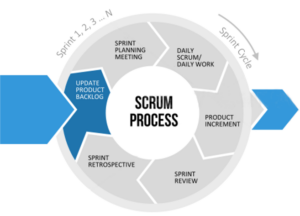
- An ordered list of everything might be necessary in the product
- Product Backlog is dynamic, it is never complete